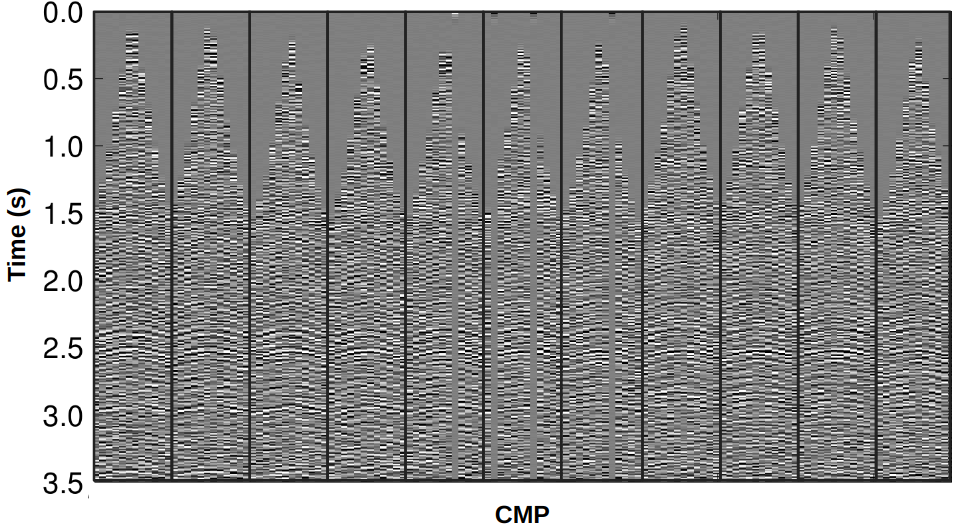
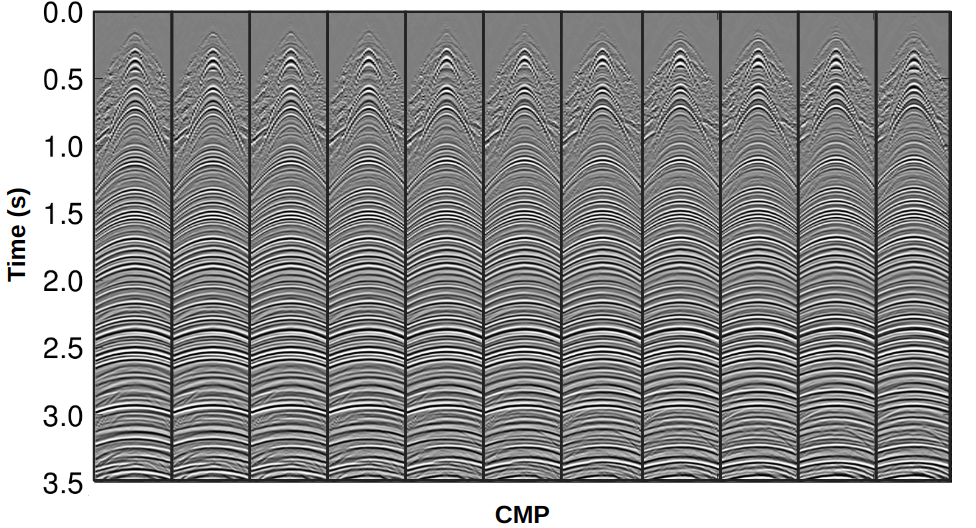
Finite Offset (FO) Stacking and Regularization
2D/3D Common Reflection Point (CRP) Regularization
The 2D/3D CRP Regularization technology is based on Common-reflection-point (CRP) Trajectories. This approach ensures that only the amplitudes related to the same reflection point are considered on the regularization process, avoiding reflection-point dispersal on dipping reflectors.
- Based on CRP trajectories.
- Enhancement of events.
- Dataset regularization and interpolation.
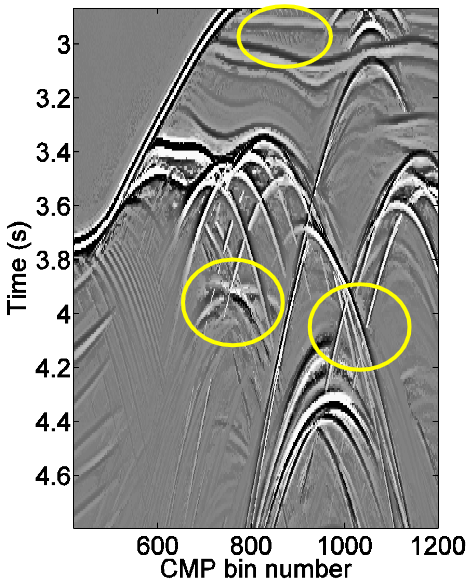
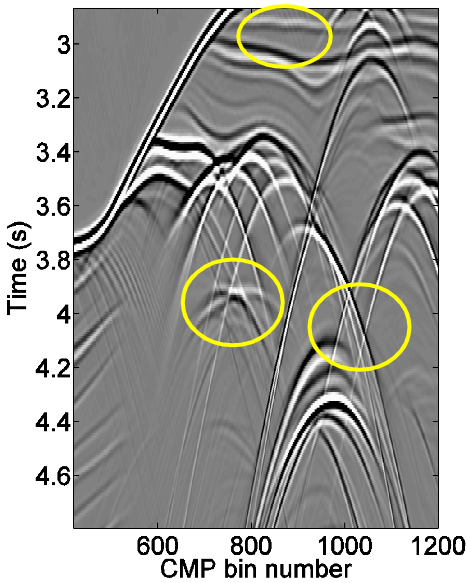
2D/3D Common Reflection Point (CRP) Spreading
The 2D/3D CRP Spreading technology is based on Common-reflection-point (CRP) Trajectories allows for reflection enhancement in prestack domain.
- Based on CRP trajectories.
- Noise attenuation.
- Enhancement of events.
- Correct conflicting dips.
HPC and Cloud Computing
SPITZ Programming Framework
SPITZ is the HPG's solution to bring modern software features and the best programming practices to a wide range of HPC systems, from the legacy ones to the newest. We extracted the essence from most seismic imaging software and created a complete distributed programming framework that is easy to use, scalable, resilient, and dynamic in nature.
- Compatible with Cloud environments and legacy systems
- Removes the programming effort of handling with distributed computing environments
- Facilitates the development and debugging of new software
- Allows seamless aggregation of multiple computing systems to form a single computing mesh
- Handles node addition, removal, and failure automatically and on-the-fly
- Optimizes cost-benefit dynamically on heterogeneous systems like the Cloud
ZO Stacking
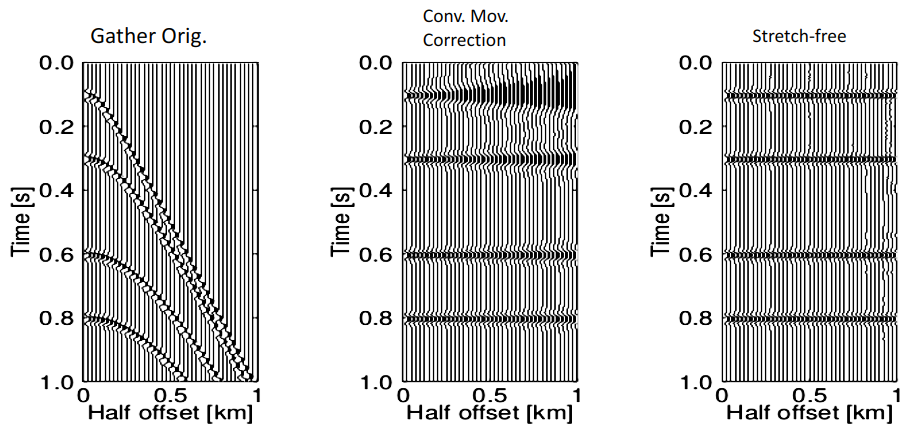
Stretch-Free Stacking
The Stretch-free Stacking technology allows for stretch-free moveout corrections that can be applied to any traveltime approximation. This technique can be incorporated into any seismic-processing sequences since it requires no changes in the estimation of traveltime parameters. The Stretch-free moveout correction is performed on a separate procedure where the required stretch-free parameters are computed automatically, considering the previously estimated moveout parameters.
- Elimination of moveout correction stretching factor.
- Applicable to any traveltime approximation.
- Can be incorporated into any seismic-processing sequence.
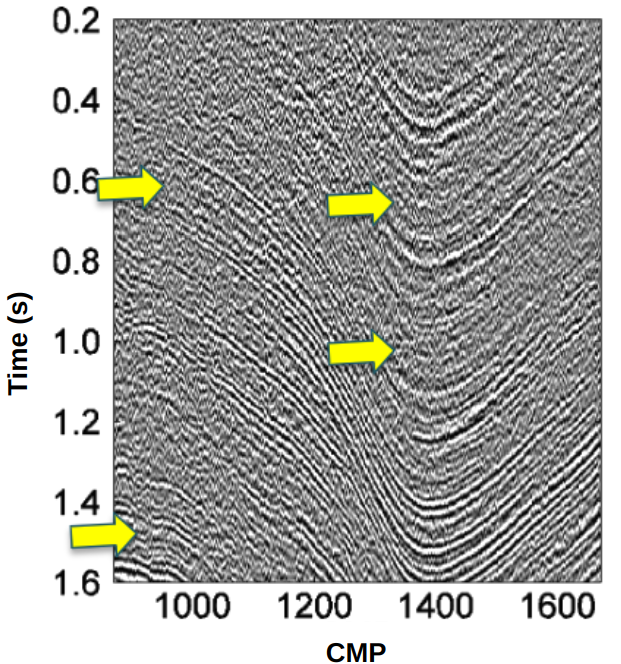
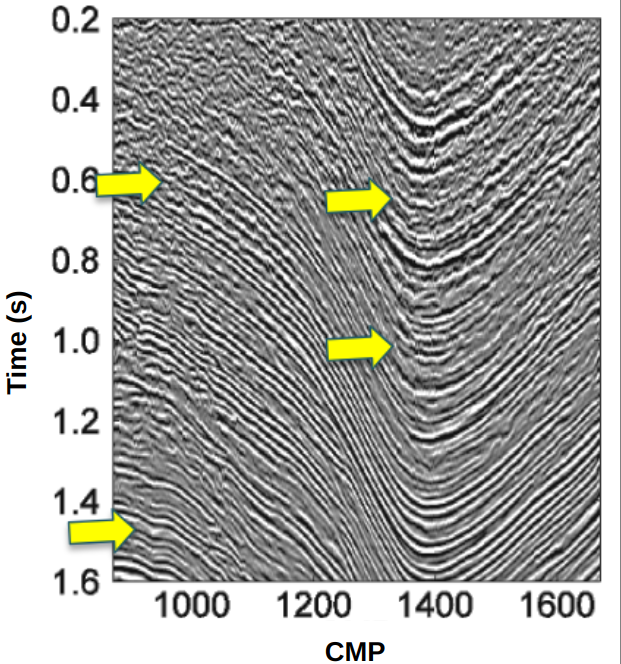
2D/3D Common Reflection Surface (CRS) Stacking
The 2D/3D CRS Stacking is a multiparametric traveltime stacking for reflections. The Common-Reflection-Surface (CRS) traveltime makes full use of redundancy available in the data, once it considers both midpoint and offset apertures around the central point, providing an enhancement on the signal to noise ratio. Furthermore, parameter guides ensure geological consistency and estimation convergence during the estimation of CRS parameters.
- Full use of redundancy available in the data.
- Parameter guides that ensures geological consistency and estimation convergence.
- Global estimation of parameters through Differential Evolution (DE).
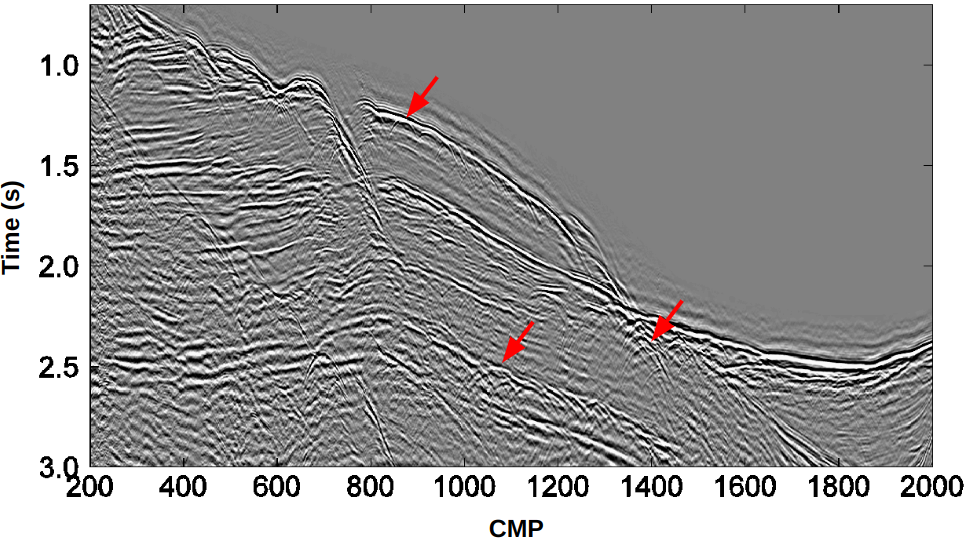
2D/3D Double Square Root (DSR) Stacking
The 2D/3D DSR Stacking performs the full stacking, in prestack domain, of diffractions considering the Double Square Root (DSR) moveout.
- Multiparametric traveltime stacking for diffractions in prestack domain.
- Superior approximation for diffraction events in prestack domain.
- Global estimation of parameters through Differential Evolution (DE).

2D/3D Double Square Root (DSR) Spreading
The 2D/3D DSR Spreading technology allows the enhancement of diffractions. The stacking process uses a DSR diffraction traveltime, in prestack domain The spreading procedure has a similar structure as the ones used in Kirchhoff migration. The better-resolved diffractions can be used to determine fault-planes, pinch-outs, discontinuities and perform quality control for time/depth migration, providing update migration velocity models.
- Enhancement of diffractions.
- Determine fault-planes, pinch-outs, discontinuities.
- Perform quality control for time/depth migration.